- BOJ 30027
- 2025acpc
- 2023 SW - IT Contest
- 세그먼트 트리
- K8s
- BOJ 30026
- 누텔라트리(hard)
- 27173
- 컴퓨터융합학부
- hhs2003
- voronoi diagram
- CodeForces
- dx dy
- 느리게 갱신되는 세그먼트 트리
- boj 30788
- fortune's algorithm
- 충남대학교 2023 SW - IT
- Delaunay triangulation
- BOJ 31226
- 오일러투어트리
- BOJ 30029
- 27114
- 알고리즘
- boj23054
- solved.ac
- 2023 Engineering Pair
- 수열과 쿼리 43
- BOJ17139
- 백준
- BOJ 30028
황현석 일지
BOJ 23054 - 누텔라 트리 (Hard) 본문
문제 링크
23054번: 누텔라 트리 (Hard)
boj.ma
문제 풀이
신나게 떠들던 와중, 이 문제를 알게 되어 잡게 되었다. 푸는데 한달정도 걸렸다.
나는 이 문제를 EulerTour Tree (ETT)로 풀었다. 즉, 독자분들이 대부분 아는 EulerTourTrick (ETT) 와는 다른 별개의 굉장히 하드코어한 알고리즘을 다룬다.
EulerTourTree 는 SplayTree를 사용하여, 간선을 관리하는 자료구조 이다. EulerTour경로를 순서대로하여, 이용한 간선과 그 방향을 순서대로 다 저장하는 방법을 사용한다. 굉장히 어려운 알고리즘이다.
이 알고리즘을 응용하여 풀어 볼 수 있는 문제로는 27974번: 트리와 쿼리 21 가 있다.
오일러투어트리의 구현에 관한 내용은 차후에 블로그에 서술하겠다.
관련 자료 [Tutorial] Euler Tour Trees (maintaining dynamic trees through their euler tour)
일단 이 문제의 EASY 버전을 살펴 보자. 23040번: 누텔라 트리 (Easy)
문제를 보면 알 수 있겠지만, NAIVE 하게 , 검은색 점 마다 시작해서, 빨간색으로 연결되어 있는 모든 컴포넌트의 갯수를 새면 된다. 이것의 시간을 줄이기 위해 빨간색 컴포넌트끼리 서로 UnionFind 로 합쳐주어서 해결하면 된다.
HARD를 살펴보자.
정점의 색깔이 바뀔 때 마다, 경로의 갯수를 구해야 한다. EASY에서 이런 변화 하나 준다고 난이도가 정말 극적으로 어려워 졌다. 아쉽게도 일주일 고민하고 갈피도 못잡아서, 태그를 깟다. 그리하여, 센트로이드로 푼다는 것을 알고 시작하게 되었다.
독자는 센트로이드 분할류 문제를 풀어본 경험이 있는가? 없다면 먼저 배우고 오는 것을 추천한다. 기초 이해를 다지고 넘어가면 너무 작성하는 내가 힘들것 같다.
센트로이드 분할을 통해 문제를 해결해 보고자 한다. 트리에서 센트로이드 트리를 만들었다고 치자.
어떠한 정점 $T$에서 분할 정복을 할 때, 센트로이드 트리상에서 $T$ 의 서브트리에 속하는 노드들을 고려하여, 정점 $T$를 경유하는 경로의 갯수를 셀 것이다.
그리하여, 실제 트리의 위상으로 그 정점들을 배치 했다고 해보자.
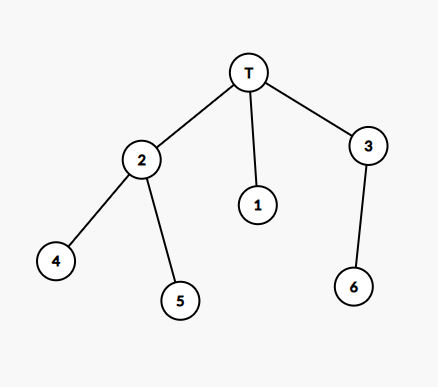
어떠한 정점 $T$에서 경로의 갯수를 찾기 위해서는 최소한의 정보들이 필요하다.
2번 정점으로 갔을 때,1번으로 갔을 때, 3번으로 갔을 때의 만날 수 있는 빨간색, 검정색 정점들의 갯수를 알아야 한다.
그럼 간단한 식정리로 T를 경유하는 경로의 갯수를 찾을 수 있다.
자 그럼 $T$에서 갈 수 있는 정점들 (자식들) 을 $T_1, T_2, T_3 \cdots T_K$ 라고 하자.
만약 어떠한 정점 $M$에 색이 변하면, 이 트리상 $M$을 서브트리 안에 가지고 있는 어떠한 정점 $T_i$ 쪽으로 가서 만날 수 있는 빨간색, 검정색 정점만 수정 하면 된다. 이 행위는 당연히 $O(\log N)$ 에 수행 되어야 한다.
이것을 어떻게 수행하여야 할 까?
$T_i$로 가는 방향만 생각해보자.

$T_i$로 가는 방향만 고려해 보자. 만날 수 있는 빨간색 정점의 개수를 어떻게 찾을 수 있을까?
만약 4번 정점이 검은색이 된다면, 그 하위 노드인 2번 8번 정점은 당연히 색깔에 관계 없이 만날 수 없게 된다.
즉, 우리는 여기서 어떠한 정점 $K$가 검은색 정점일 경우, $K$의 서브트리는 고려할 필요가 없다는 것을 알 수 있다.
자 그럼, 만약 정점 $K$가 검은색이 된다면 $K$의 서브트리를 없애자.
그러면, $T_i$와 연결되어 있는 모든 노드는 빨간색임이 보장된다. 이런 식으로 연결된 빨간색 컴포넌트 들을 관리 할 수 있다.
오일러 투어 트리를 사용하면, 어떠한 정점 $K$에 대해, 하위서브트리에 대한 정보를 $O(log N)$에 가져올 수 있다.
ex) 각 정점 모두 더하기, 빼기, 트리크기 측정
오일러 투어 트리는 링크-컷/ 연산을 지원한다. 특정 정점에 대한 서브트리에 대한 정보를 알 수 있다.
여기서 연산을 사용한다. 오일러 투어 트리 쿼리 : $K$와 그 부모의 정점과의 연결을 끊는다.
만약 $K$가 빨간색 정점이 된다면, $K$를 다시 그 부모의 정점과의 연결한다.
만날 수 있는 검은색 정점들을 구해보자. 접근할 수 있는 빨간색 정점들에 모든 자식을 더한 값을 $L$ 이라고 하자.
검은색 정점의 갯수는 $L$ - (접근할 수 있는 빨간색 정점들) $+ 1$인 것을 쉽게 알 수 있다.
이것 또한 오일러투어 트리를 관리할 때, 자식갯수도 관리하면 쉽게 얻을 수 있다.
이렇게 계산으로 하기 싫다면, $K$가 검정색 정점으로 변할 때, 부모에게 자신이 검정색 정점으로 변했다고 기록해두고, 이를 오일러투어트리 (ETT) 안의 스플레이 트리 (Splay Tree) 안에서 적절히 합쳐 준다면 간단하게 구할 수 있다.
자! 그럼 우리는 $T_i$ 방향에 있는 정점들에 대해서, 업데이트를 amortized $O(\log N)$에 수행하고, 정보를 찾을 수 있다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
|
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX =101010;
typedef long long lint;
vector<int> load[MAX];
int siz[MAX], cent[MAX], up[MAX], N, color[MAX], limit;
lint cross[MAX], answer;
//해당 센트로이드의 부모 센트로이드로 이어질 때 최상위 일반 노드를 가르킨다.
int myOrder[MAX];
//해당 센트로이드에서방향으로의 key : 노드의 value : 부모
struct eulorManager {
struct Node {
Node *p = nullptr, *left = nullptr, * right = nullptr;
Node *realp = nullptr;
Node *linked = nullptr;
int mySon=0, sumSon=0, size=1, real=0, realSum=0;
void update () {
size = 1, sumSon = mySon, realSum = real;
if (left) {
size += left->size;
sumSon += left->sumSon;
realSum += left->realSum;
}
if (right) {
size += right->size;
sumSon += right->sumSon;
realSum += right->realSum;
}
}
};
map<int, Node*> nodes;
vector<Node*> vc;
void init () {
if (vc.empty()) return;
for (int i=1;i<vc.size();i++) {
vc[i-1]->right = vc[i];
vc[i]->p = vc[i-1];
}
splay(vc.back());
}
Node* root;
void rotate (Node* a) {
Node* parent = a->p, *leaf;
if (parent->left == a) {
leaf = parent->left = a->right;
a->right = parent;
} else {
leaf = parent->right = a->left;
a->left = parent;
}
a->p = parent->p;
parent->p = a;
if (leaf) {
leaf->p = parent;
}
if(a->p) {
if (a->p->left == parent) {
a->p->left = a;
} else {
a->p->right = a;
}
} else {
//use dangerous is not a 1 set
root = a;
}
parent->update();
a->update();
}
void splay (Node* a) {
a->update();
if (!a->p) {
root = a;
return;
}
while(a->p) {
if (a->p->p)
rotate((a->p->p->left == a->p) == (a->p->left == a) ? a->p : a);
rotate(a);
}
}
void destroy (Node *x) {
splay(x);
Node *segment = 0;
int left = getOrder(x), right = getOrder(x->linked);
int limit = root->size;
assert(left != 1 && right != limit);
findKth(left - 1);
Node* original = root;
root = original->right;
root->p = nullptr;
findKth(right - left + 2);
segment = root->left;
segment->p = 0;
segment->update();
original->right = root;
root->p = original;
//remove
root->left = 0;
root->update();
root = original;
root->update();
//segment 분리됨.
}
void findKth (int order) {
//변수 order는 1-based 입니다.
Node* now = root;
while(1) {
if (now->left == nullptr && now->right == nullptr) break;
if (now->left && now->right) {
if (now->left->size + 1 == order) break;
if (now->left->size < order) {
order -= now->left->size + 1;
now = now->right;
} else {
now = now->left;
}
} else if (now->left) {
if (now->left->size + 1 == order) break;
now = now->left;
} else {
if (order == 1) break;
now = now->right;
order--;
}
}
splay(now);
}
// 특정 노드의 위치 순서를 구합니다. 1-based
int getOrder (Node *a) {
splay(a);
return a->left ? a->left->size + 1 : 1;
}
void attach (Node* from, Node* to) {
splay(from);
splay(to);
Node* rightSeg = to->right; to->right->p = 0;
to->right = from; from->p = to;
to->update();
Node* temp = to;
while(temp->right) temp= temp->right;
temp->right = rightSeg; rightSeg->p = temp;
splay(rightSeg);
}
};
eulorManager ett[MAX];
struct tree {
// it means sum of a centroids
lint ans=0, black=0, red=0;
} tree[MAX];
struct pbox {
lint red=0, black=0;
} pbox[MAX];
int dfs (int node, int prev, int centroid, eulorManager::Node *realP = nullptr) {
//모든 정보를 여기서 모은다.
int siz = 1;
eulorManager &etree = ett[centroid];
eulorManager::Node *enter = new eulorManager::Node();
enter->real = 1;
etree.nodes[node] = enter;
enter->realp = realP;
int countSon = 0;
etree.vc.push_back(enter);
for (int next : load[node]) if (next != prev && !cent[next]){
countSon++;
siz += dfs(next, node, centroid, enter);
}
enter->mySon = countSon;
enter->update();
//dummy node role's
eulorManager::Node *exit = new eulorManager::Node();
enter->linked = exit;
etree.vc.push_back(exit);
return siz;
}
int getSize (int node, int prev) {
siz[node] = 1;
for (int next : load[node]) if (next != prev && !cent[next]){
siz[node] += getSize(next, node);
}
return siz[node];
}
int findCent (int node, int prev) {
for (int next : load[node]) if (next != prev && !cent[next] && siz[next]*2 > limit){
return findCent(next, node);
}
return node;
}
void update (int x) {
answer -= tree[x].ans;
if (color[x]) {
//red
tree[x].ans = (1 + tree[x].red) * tree[x].black - cross[x];
} else {
tree[x].ans = tree[x].red;
}
answer += tree[x].ans;
int centroing = up[x], prevCent = x;
while(centroing != 0) {
eulorManager &etree = ett[centroing];
//해당방향 수정해주어야함.
int higher = myOrder[prevCent];
if (x != higher) {
if (color[x]) {
//센트로이드 방향의 부모에게 attach 함
etree.attach(etree.nodes[x], etree.nodes[x]->realp);
} else {
etree.destroy(etree.nodes[x]);
}
}
//pbox 수정해야함
auto &used = pbox[prevCent];
tree[centroing].red -= used.red;
tree[centroing].black -= used.black;
cross[centroing] -= used.red * used.black;
lint red, black;
if (!color[higher]) {
red = 0;
black = 1;
} else {
etree.splay(etree.nodes[higher]);
red = etree.root->realSum;
lint temp = etree.root->sumSon;
black = temp - red + 1;
assert(black >= 0);
}
used.red = red;
used.black = black;
cross[centroing] += used.red * used.black;
tree[centroing].red += used.red;
tree[centroing].black += used.black;
answer -= tree[centroing].ans;
if (color[centroing]) {
tree[centroing].ans = (1 + tree[centroing].red) * tree[centroing].black - cross[centroing];
} else {
tree[centroing].ans = tree[centroing].red;
}
answer += tree[centroing].ans;
centroing = up[centroing];
prevCent = up[prevCent];
}
}
int dnctree (int node, int prev) {
limit = getSize(node, -1);
int centroid = findCent(node, -1);
cent[centroid] = 1;
int count = 0;
vector<int> vc;
for (int next : load[centroid]) if (!cent[next]) {
int siz = dfs(next, centroid, centroid);
ett[centroid].init(); ett[centroid].vc.clear();
vc.push_back(siz);
}
int idx = 0;
for (int next : load[centroid]) if (!cent[next]){
int nextCent = dnctree(next, node);
myOrder[nextCent] = next;
up[nextCent] = centroid;
count++;
int siz = vc[idx++];
pbox[nextCent].red = siz;
tree[centroid].red += siz;
}
return centroid;
}
int main () {
cin.tie(0);ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> N;
int u, v; char k;
for (int i=1;i<N;i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
load[u].push_back(v);
load[v].push_back(u);
}
for (int i=0;i<=N;i++) color[i] = 1;
int root = dnctree(1, 0);
for (int i=1;i<=N;i++) {
cin >> k;
if (k == 'B') {
color[i] = 0;
update(i);
}
}
cout << answer << '\n';
int Q;
cin >> Q;
while(Q-->0) {
cin >> u;
color[u] ^= 1;
update(u);
cout << answer << '\n';
}
}
|
cs |
오일러 투어 트리 사용해서, 문제 이상하게 푸는놈은 나밖에 없다.
끝.
'알고리즘 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| EPIC Institute of Technology Round Summer 2024 (Div. 1 + Div. 2) D. World is Mine (2) | 2024.07.20 |
|---|---|
| BOJ 1514 - 자물쇠 (0) | 2024.07.18 |
| BOJ 17139 - 초라기와 쿼리 (0) | 2024.04.09 |
| BOJ 31226 - 고슴도치 그래프 2 (0) | 2024.02.29 |
| BOJ 9250 - 문자열 집합 판별 (1) | 2024.01.11 |


